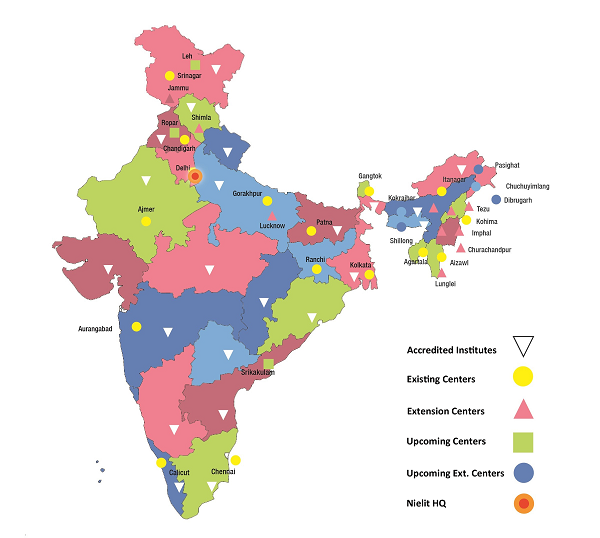
ESDM100
Spot Admission is open till Sep 18th-Guidelines
Download Course Prospectus(139 kB) Online Application
Preamble
Electronics and Hardware Industry is increasingly finding applications in all sectors of the economy and thus is accepted as a key enabler in development of our country. The current growth trend and its existing contribution to the global electronics industry indicates that the share of IT Hardware and Electronics and Manufacturing in India, in terms of output and employment, has the potential to grow manifolds, driven by its emergence in the global electronics manufacturing value chain.
In order to create a conducive environment for manufacture of high technology,capital intensive semiconductors and other high tech electronic products, attract global investments as well as bridge the viability gap due to lack of adequate infrastructure and ecosystem, Government of India has announced number of initiatives in the country. To this aspect, there is also a need to ensure availability of trained human resources for this sector in order to sustain growth and to achieve the target set for this sector
Course Objectives
It is proposed to offer PG Diploma in Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) to enable new Electronics graduates/post graduates or working engineers in electronic industries to specify, design, develop and test electronic products. This is offered to bridge the major gap in competencies required to design, manufacture and market Indian state-of-the art electronic products.
The focus of the proposed program will be state-of-the-art electronic products that are likely to be manufactured in medium and large volumes for Indian and Global markets such as automotive, medical, consumer, industrial, entertainment, aerospace and defense. The program will not emphasize complex products produced in small numbers or very complex systems (main frame computers, telephone exchanges, data centers etc.).
The representative product for consideration in this program include music systems,biomedical equipment, cell phones, laptops, PCs, tablets, set top boxes, TV sets, modems, instrumentation systems ,routers, controllers, RFID systems, smart card related equipment, UPS, power management systems. The program is also restricted to the design of products that are based on known technologies of manufacturing and available components.
Course Outcome
On successful completion of the Course, the Participants shall get
-
Exposure to Electronic Product Design process and Manufacturing
-
Exposure to Processor/FPGA based Embedded System design
-
Expertise in Embedded Software development/Digital Signal Processing/Power management/Communication Interface/IOT.
Course Structure
This course consist of eight (Four Core and three Elective) modules including project. Out of three elective modules two modules should be from ESDM 105, ESDM106 or ESDM 110 and one module from ESDM 107, ESDM108 or ESDM 109. Studentshave an option to select those electives.
| ESDM 100 | Module name | Duration |
|---|---|---|
|
ESDM 101 |
Fundamentals of Electronics(core) |
3 weeks |
|
ESDM 102 |
Electronics System Packaging and Manufacturing (core) |
2 weeks |
|
ESDM 103 |
Industrial Electronic Product Design (core) |
2 weeks |
|
ESDM 104 |
Processor based System Design (core) |
3 weeks |
|
ESDM 105 |
FPGA based System Design (elective) |
3 weeks |
|
ESDM 106 |
Embedded Software Development (elective) |
3 weeks |
|
ESDM 107 |
Embedded Digital Signal Processing (elective) |
2 weeks |
|
ESDM 108 |
Power management of Electronics Products (elective) |
2 weeks |
|
ESDM 109 |
Communication interface of Electronics Products (elective) |
2 weeks |
|
ESDM 110 |
IOT (elective) |
3 weeks |
|
ESDM 111 |
Project |
6 weeks |
Course Contents
Module 1 – Foundation for Electronics System Design
- Electronics Fundamentals
Material classification based on conductivity, basic Semi-conductor, Diodes,Characteristics of Diodes, Classification of Diodes, Transistors, Classification of Transistors, BJT characteristics, JFET & MOSFET Characteristics, Transistor Amplification Circuits, OP Amp, Basic Characteristics of OP Amp, Feedback circuits,Introductions to Digital circuits.
- Fundamentals of circuit design
Basic circuit laws , Current & voltage division Rules, Introduction to Linear andNon-linear elements, Classification of sources, Equivalent Impedance Calculations inseries & parallel circuits, Basic Network Theorems,Current, voltage and Power calculations in a circuit, Diode applications,Clipping and Clamping Circuits with Diodes, Rectifier Circuits, Transistors, Selection and analysis of Components, sensing devices and display devices.
- Module-2 (Electronic System Packaging and Manufacturing)
Evolution and Classification of Printed Circuit Boards, Challenges in ModernPCB Design and Manufacture, PCB fabrication methodologies(SSB, DSB and multilayerboard), PCB design considerations/ design rules for analog, digital and power applications, Electromagnetic interference in electronic systems and its impact. Analysis of electronic circuit from noise emission point ofview (both conducted and radiated emission) cross talk and reflection behavior of thecircuit in time domain, Thermal management of electronic devices and systems.
- Semiconductor Packages:
Single chip packages or modules. (SCM) Commonly used packages and advanced packages; Materials in packages, Current trends in Packaging, Multichip modules (MCM)-types; System-in package (SIP); Packaging roadmaps; Hybrid circuits
- Module-3 (Industrial Electronic Product Design)
Development Process, Product Planning & Conceptualization, Product Architecture and Industrial Design, Product Manufacturing & Prototyping, Economic Analysis & Managing Projects. Introduction to 3-D printing and Rapid Prototyping.
- Module-4 (Processor based System Design)
Introduction to ARM Processor architecture and programmer’s model, Overview of Cortex Architecture, Cortex M3 Register Set and Modes, Cortex M3 Processor Core,Data Path and Instruction Decoding, ARM Cortex M3 Development Environment, Assembler and Compiler, Linkers and Debuggers, ARM,
Thumb & Thumb 2 instructions, Mixing ARM & Thumb Instructions, Memory hierarchy,Memory Mapping, Cache.
Programming Concepts: – High level and low level languages, Compiler, Linker & Cross compilers, running, debugging and testing of programs, Measures of program performance, Program optimization techniques.
Programming using Assembly language, C Programming: Introduction, Data Types andstorage classes, Controlling program flow, Arrays,Functions, Pointers, Arrays and Pointers, Pointer to Functions and advanced topics on Pointers, Structures and Unions, Preprocessor directives, File operations, bitwise operations, Typecasting.
Cortex M3 based controller architecture, Memory mapping, Cortex M3 Peripherals – RCC, GPIO, Timer, System timer, UARTs, LCD, ADC, Cortex M3 interrupt handling –NVIC. Application development on Cortex M3 controllers.
Elective Modules
- Module-5 (FPGA based System Design)
Introduction to FPGA, HDL Refresher, Introduction to modeling & Writing Simple Test Benches, FPGA Devices, Design Flows, Principles of Combinational Circuit Design, Principles of Sequential Circuit Design, Principles of FSM Design, Principles of RTL Design, Mixing Design Styles, HDL Coding for Sy
nthesis, Designing Memories, Modeling of Microprocessors, Designing SoC based system, Designing Bus based systems, Interfacing peripherals with the SoC, Interrupt Mechanisms with Processor.
- Module-6(Embedded Software Development)
Operating System Concepts for Embedded Systems Basic Operating System Concepts: Linux as Embedded OS, Comparison of Embedded OS, Embedded OS Tools and development, Discussion on Embedded OS Applications and products, System Calls, Linux Compiler options, Make.
Internals of Linux OS: Process, Multithreading and Synchronization.
Inter Process Communication:
Pipe and FIFOs, Shared memory, Sockets.
etting Linux on a device and Driver Development
Introduction to Linux Kernel source tree and compilation, Linux boot sequence, Building Kernel, Building Boot image, Linux Kernel modules and module programming, Linux Device drivers
RTOS Concepts
Introduction to Real-time systems and Embedded Real-time Systems, Discussion and Comparison of popular RTOS, Design Goals for Real-time software, Discussion onEmbedded Real-time applications, Considerations for real-time programming,
Task/Thread Creation and management, Inter Task/Process Communication Mechanisms,
Semaphores, Message Passing, Pipes, Interrupts, Development Tools.
Porting
Building root file system, Kernel Compilation for ARM, Porting of Embedded OS on ARM
Module-7 (Embedded Digital Signal Processing)
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
Discrete-time signals, Signal classification, Discrete-time systems, Sequences,Representation of signals on orthogonal basis, Sampling and reconstruction of signals. Time-Domain, Frequency Domain, Differential equation and Difference equation. MATLAB based examples
Z-Transform, Analysis of LTI systems, Frequency analysis, Inverse Systems,Discrete FourierTransform (DFT), Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm,Implementation of DiscreteTime Systems. MATLAB based examples, demonstrationsand exercises on real sensor data. Different implementation techniques for real time systems.
Digital Filter Design
Design of FIR Digital Filters (windows, frequency sampling, Remez algorithm and least meansquare error methods), Design of IIR Filters ( Butterworth, Chebyshev andElliptic Approxi-mations; Lowpass, Bandpass, Bandstop and High pass Filters). Effect offinite register lengthin FIR Filter design. Introduction to multi rate signal processing. Adaptive Filter design. Different implementation techniques for real time systems.Optimization methods for real time implementation on embedded platform.
DSP System Design and Realization techniques DSP System Design and Realization Techniques, Arithmetic issues, pipelining,memory hierarchy, Harvard architecture and parallel processor realizations, digital signal processors, porting issues of signal processing algorithms on embedded DSP platform,
Optimization techniques:Memory optimization for embedded application, Run TimeOptimization. Fixed point implementation for different DSP algorithms
- Module-8 (Power management of Electronic Products)
Introduction to low power design techniques and methodologies
Introduction to various types of power supplies.
Estimation of power supply requirements and power loss in electronic products.
Selection of appropriate power supplies for the given primary power sources. (220VAC/Battery) Design of power scheduler, power management unit of an electronic product
- Module-9 (Communication interface of Electronic Products)
Introduction to serial (wired and wireless) and parallel communication.
Familiarization of Serial communication protocols: I2C, SPI Ethernet, USB, PCI and PCIe. TCP/IP communications model and functional properties of each one of the layers. Packet and file transfer using embedded web server which supports FTP/HTTP/ SMTP/SNMP protocols.
- Module-10 (Internet of Things (IOT) Technology for Electronic Products)
Fundamentals of Wireless Technologies Evolution of Wireless Communication, RF fundamenta
ls, Overview of Cellular Systems, 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th Generation Cellular Systems.
- Network Devices and the Internet of Things:
Computer networking overview: TCP/IP, IPV6, Networking devices, topologies. IoT Wireless Technologies: IoT Wireless standards, Wireless LANs: 802.11,802.11a/b/g/n, Wireless Personal Area Networks, Bluetooth, IEEE 802.15 standards, Zigbee, Sensor Networks.
IoT overview: IoT Entities, IoT standards, IoT application development withEmbedded hardware ( Intel Galileo & ARM Cortex Controllers)
Eligibility
B.E/ B.Tech/ B.Sc/ MSc/ Engineering Graduate/ PG in Electrical/Electronics/ Electronics and Communication/ Bio-Medical Engineering/ Medical Electronics/ Electronics and Instrumentation/ Computer Science and allied branches.
Fees
General Candidates : 60, 000 + Service tax at actual *
SC/ST Candidates : 6840*
*Service Tax is presently 14% and revised rates are applicable as per Govt of India Orders
** For SC/ST Category Applicants: Tuition Fees/Examination fees are waived for SC/ST students admitted under SCSP/TSP. However they are required to remit an amount of Rs 6,840 as Advance caution/security deposit. This amount will be considered as caution/security deposit and will be refunded after successful completion of the course. If the student fails to complete the course successfully this amount along with any other caution/security deposits by the student will be forfeited.
See course brochure for Course Fee Installment Structure
Important Dates
|
Last date for receiving completed application forms |
First selection list will be prepared based on the applications received on or before 27th July 2015. The additional selection list will be prepared based on the applications received on or before 10th Aug 2015, and excluding the applicants, included in the first selection list. |
|
Publication of first selection list in theWebsite http://calicut.nielit.gov.in/ |
27th July 2015 |
|
Last date for taking provisional admission by paying Advance Deposit (Rs 10000/-), for applicants in the first selection list |
3rd Aug 2015 |
|
Publication of additional selection list in our website (if there are vacant seats) |
10th Aug 2015 |
|
Counseling date |
7th Sept 2015 |
|
Class Commencement date |
8th Sept 2015 |
|
Payment of Advance Deposit for applicants in first selection list |
On or before 3rd Aug 2015 |
|
Payment of first installment fees |
On or before 7th Sept 2015 |
|
Payment of second installment fees |
On or before 09th Nov 2015 |
More Details
For more details like How to Apply, Placement, Hostel, etc please see the Course Calendar or Course Brochure(139 kB)
For more Information Contact the course coordinator,
Nandakumar.R
Ph # 9995427802,0495-2287266 Extn 244
Email: nanda@calicut.nielit.in, nanda24x7@gmail.com