Big Data Analytics
BigData Technology | Government of India : National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology
| Introduction: In today’s world where data is the new oil, big data can hypothetically be assumed as a system that acquires crude oil and makes fuel out of it. Big Data simply refers to a large amount of data which is of structured, semi-structured or unstructured nature. The data pool is so voluminous that it becomes difficult for an organization to manage and process it using traditional databases and software techniques. Therefore, big data not only implies the enormous amount of available data but it also refers to the entire process of gathering, storing, and analysing that data. Today’s business enterprises are data-driven and without data no enterprise can have a competitive advantage. Today, Big Data is so rampant that one has to look which are the companies that are not deploying Big Data. | |
 |
|
|
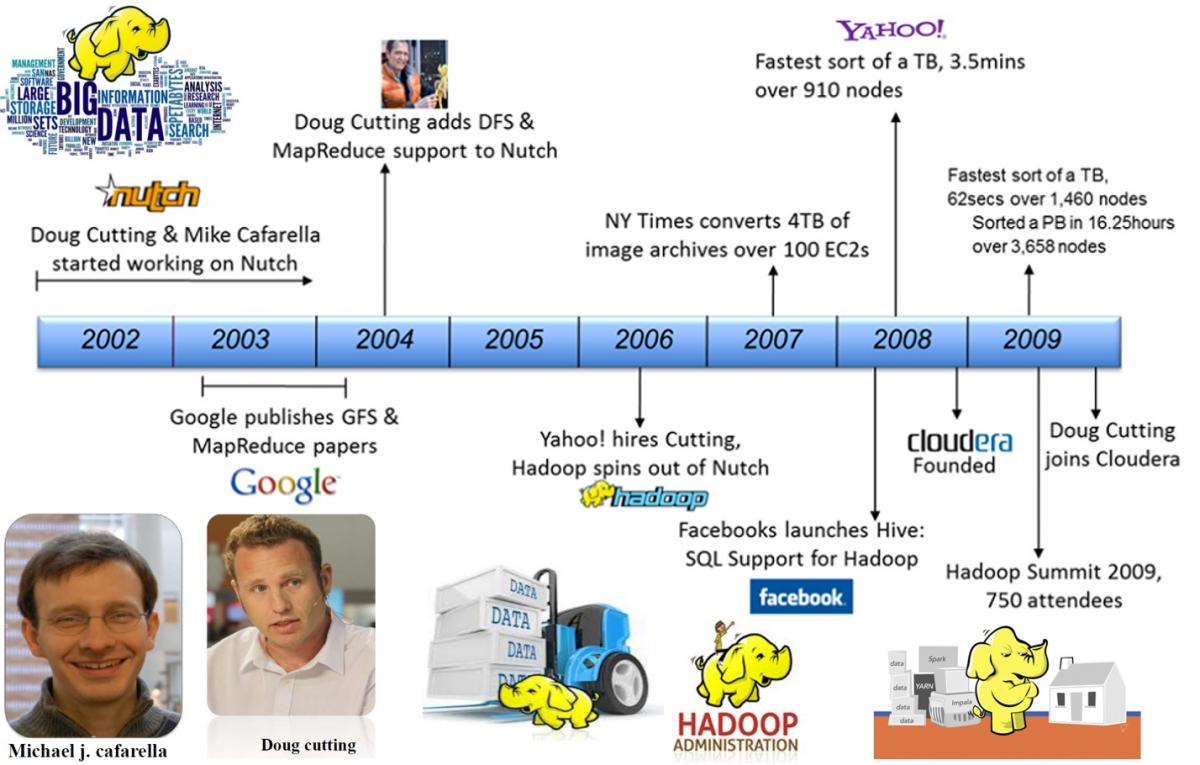
1. History: Hadoop was created by Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella in 2005. Doug, who was working at Yahoo! at the time named the project after his son's toy elephant who was 2 years old at the time and just began to talk. In 2007, Yahoo started using it. In January, 2008,
Yahoo released Hadoop as an open source project to ASF(Apache Software Foundation). In July, 2008, Apache Software Foundation successfully tested a 4000 node cluster with Hadoop. Apache Hive was co-created by Joydeep Sen Sarma and Ashish Thusoo in 2006 during their stint at Facebook to handle gathering data and ingesting it into Hadoop that was incoming at the rate of around 15 TBs/day.
Pig started out as a research project in Yahoo! in 2006. In 2007, Pig was open sourced via the Apache Incubator. In September 2008 first Pig release came in. The Spark got initiated as one of the research projects in 2009 at University of California, Berkeley’s AMP Lab. It was later open-sourced in 2010. Spark grew and moved to Apache Software Foundation in 2013. |
2. Significance of Big Data in India: With a population of around 1.3 billion, Big Data holds a significant position in the Indian context. As per the study conducted by NASSCOM, “the Indian analytics industry is predicted to reach $16 billion mark by 2025”.
NITI Aayog is developing “National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP)” with a vision to Democratize access to public Government data through a world-class user experience. Mission is to Standardize data across multiple Government sources to provide flexible analytics and make it easily accessible in formats conducive for research, innovation, policy making and public consumption.
When it comes to job positions and roles, Big Data is one of the most versatile career options. As Analytics is a crucial tool used in many different fields, you get a host of job titles to choose from including Big Data Engineer, Big Data Analyst, Big Data Analytics Architect, Big Data Solution Architect, Analytics Associate, Metrics and Analytics Specialist, Big Data Analytics Business Consultant, Business Intelligence and Analytics Consultant to name a few. |
 |
 |
|
3. Apache-Pig: Apache Pig is helpful for the analysis of huge datasets. It reduces the length of codes and using Pig Latin programmers can easily write complex MapReduce tasks. PIG is more like PL/SQL and is a Data Flow language. Pig Latin can be extended using user-defined functions (UDFs) that the users can write in Java, Python, JavaScript, Ruby, or Groovy. There are many organizations including Twitter, Yahoo, LinkedIn, Mendeley to name a few that uses Pig for finding or matching relevant data. |
 |
|
4. Apache-Spark: Apache Spark is mainly used to redefine better customer experience and provides a lightning-fast computing framework for data processing. Spark and Hadoop together make a powerful combination to handle Big Data Analytics. Spark will be preferred for real-time streaming and Hadoop will be used for batch processing. The most interesting fact here is that both can be used together through YARN.
Spark supports programming languages like Python, Scala, Java, and R. Spark can be deployed in numerous ways like in Machine Learning, streaming data, and graph processing. |
5. Why BigData is Important? It helps in 5.1 Proactively engaging with the customer. 5.2 Generation of new revenue streams 5.3 Product and service redesign to meet customer needs 5.4 Removing biasness in favour of big players. 5.5 Streamlining the business processes. 5.5 Maintaining a business to keep it in sync with the changing times 5.6 Making better decisions, as well as verify & disprove existing models. |
 |
|
|
6. Skill-Sets to be imparted:
|
8. Online Course Offered by NIELIT:
|
|
7. References: https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2020-01/Vision_Document_30_Jan.pdf http://dgace.cag.gov.in/pdf/Big-Data.pdf https://cis-india.org/internet-governance/files/big-data-compilation.pdf http://archive.apache.org/dist/ http://apachemirror.wuchna.com/pig/ https://www.edureka.co/blog/apache-hive-installation-on-ubuntu https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_data https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Presentations http://archive.apache.org/dist/hive/hive-0.14.0/ https://www.edureka.co/blog/apache-hive-installation-on-ubuntu |
Registration and Contact Details Ms Meenu Dhir, Joint Director - +91-9779131848 Sh Sachin Chandla, Joint Director - +91-7696044044
Sample Reading Material Module 1-Introduction to BigData |