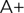Engineering Visualization
|
1. Course Objectives: To build the foundations for engineering visualization by familiarizing the students with engineering drawings and tools/instruments of practice. Provide hands-on training to develop foundational skills in 3D modelling, using popular computer-aided design (CAD) packages. Equip students with the ability to create basic 3D models, modify designs, and understand the transition from 2D drawings to 3D digital representations. Encourage practice in building models from drawings and converting conceptual designs into virtual prototypes. This structure not only covers the fundamental skills of engineering visualization but also ensures that students understand the real-world applications of these concepts. |
||
|
2. Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to |
||
|
CO-1: Understand the tools and instruments commonly used in professional engineering drawing practice (e.g., drawing boards, compasses, scales, and CAD software).
CO-2: Create and read professional engineering drawings.
|
CO-3: Visualize the product in various ways. CO-4: Create 3D models for their (future) designs. CO-5: Improve the design, analysis, communication, and implementation of complex systems, which turn abstract concepts into clear, tangible representations that can be analysed. |
|
|
3. Main Equipment’s / Software’s Available Tools and Software Commonly Used in Engineering Visualization:
|
||
|
3.1. 50 Dell desktops of core i7 Intel 3.60 connected to 24x7 1GBPS high-speed Internet connections. The Dell's Intel Core i7 Desktops are optimized for content streaming, with features like high-quality displays, advanced graphics, and fast connectivity. |
|
|
|
|
3.2. Sony VPL-EW246 Video Projector: The VPL-EW246 is economically designed with a compact body filled with energy and cost saving features. In addition, a variety of network functions, rich inputs and outputs are available. This model is an excellent choice for education and business. It is a compact data projector that delivers exceptional image quality with eco-conscious features. In addition, a variety of network functions such as web control, network presentation and wireless presentation from mobile device can be performed. |
|
|
3.3. FreeCAD is a free parametric 3D computer-aided design (CAD) modelling tool used to create objects ranging from simple designs to complex projects consisting of extensive assemblies of numerous parts. Due to its open-source nature, FreeCAD can be used for both personal and commercial purposes. This makes FreeCAD an appealing option not only for relatively inexperienced users, such as hobbyists in the 3D printing world, but also for experienced users looking to experiment with a different parametric tool. |
|
|
|
3. Course Exercises: |
5. Suggested Books: |
|
|
3.1. Topic: Projection of Points. 3.2. Topic: Projection of Lines. 3.3. Topic: 3D Solid Model. 3.4. Topic: 2D and 3D Drawing. 3.5. Topic: Advance 3D Drawing. 3.6. Topic: Projection of Solids. 3.7. Topic: Isometric Views from projections. 3.8. Topic: Sectional Views. 3.9. Topic: Dimensioning and Detailed Drawing. 3.10. Topic: Assembly and Assembly Drawings |
1. N. D. Bhatt, Engineering Drawing, Charotar Publishing House, 2014 2. D. K. Lieu and S. Sorby, Visualization Modeling and Graphics for Engineering Design, Cengage Learning, 2015 3. D. C. Planchard, M. P. Planchard, Egineering Graphics with Solidworks (A step-by-step Project Based Approach), SDC Publications, 2013. 4. E. Finkelstein, “AutoCAD 2007 Bible”, Wiley Publishing Inc., 2007. |
|
|
FACULTY COORDINATOR: Dr. L. Shyam Sunder Singh LAB INCHARGE: Mr. Mukul Sharma |
LAB CO-INCHARGE: Ms. Anushree PLACE: Room#10, Ground Floor, CSED@NIELIT |
|