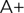Engineering Physics Lab
|
1. Course Objectives: To impart physical measurement skills. Develop the skills needed to set up the equipment required to test models or theory developed in the lecture course. Be able to interpret results and develop correct conclusions. Maintain a laboratory notebook and write formal reports of practical. |
|
|
2. Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of the course/Lab the students will be able to |
|
|
CO1: Understand and Develop skills to impart practical knowledge in real time solutions. CO2: Understand principle, concept, working and application of new technology and comparison of results with theoretical calculations. |
CO3: Gain knowledge of new concept in the solution of practical oriented problems and to understand more deep knowledge about the solution to theoretical problems. CO4: Understand measurement technology, usage of new instruments and real time applications in engineering studies. |
|
3. Main Equipment’s/Software’s Available |
|
|
3.1 Interferometer: Interferometers are investigative tools used in many fields of science and engineering. Pioneered in the mid- to late-1800s, they are called interferometers because they work by merging sources of light to create an interference pattern, which can be measured and analyzed: hence 'Interfere-meter', or interferometer. |
|
|
|
3.2 Newton's rings: Newton's rings is a phenomenon in which an interference pattern is created by the reflection of light between two surfaces, typically a spherical surface and an adjacent touching flat surface. When viewed with monochromatic light, Newton's rings appear as a series of concentric, alternating bright and dark rings centered at the point of contact between the two surfaces. |
|
3.3 Junction diode: On the basis of the type of impurities added, the semiconductors are classified as p-type (positively charged) and n-type (negatively charged). When the p and n types are fused together, it forms a "p-n junction semiconductor." When a p-n junction semiconductor is affixed to an external voltage source, it is called a "p-n junction diode." The p-n junction diode is an interface between an n-type and a p-type semiconductor material |
|
|
|
3.4 Spectrometer: A spectrometer is an analytical instrument used to measure the properties of light across a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. It separates light into its component wavelengths (or frequencies) to analyze the spectral content.
|
|
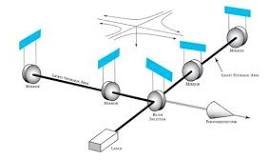
3.5 He-Ne laser: The excitation mechanism involves electrons colliding with helium atoms to produce helium metastable atoms, which then transfer their energy to neon laser levels. This laser is used in surveying, construction, supermarket checkout scanners, printers, and many other applications. |
|
|
4. Suggestive List of Experiments |
|
|
|
|
5. Suggested Books: |
6. References |
|
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-interferometric-modulator/ 2. Newton's rings. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/program-for-newton-raphson-method/ 3. Juction diode. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/applications-of-pn-junction-diode/ 4. Spectrometer. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/infrared-spectroscopy/ 5. He-Ne laser. https://physicsgirl.in/helium-neon-he-ne-laser-construction-working-principle-applications-and-energy-level-diagram/ |
|
FACULTY COORDINATOR: Dr. L Shyam Sunder Singh LAB INCHARGE: Kamlesh Kumar Samota |
LAB CO-INCHARGE: Kamlesh Kumar Samota PLACE: Room#10, 1st Floor, CSED@NIELIT |